The Rise of India’s Coffee Industry: Insights and Trends 2025
Author: John P. LaWare
Nowadays India is a major Coffee producer in the world with 374 thousand metric tons coffee production in year (2024). As a seasoned market analyst with decades of experience in the coffee industry, I have witnessed India’s remarkable journey from a minor player to a significant contributor in the global coffee market. In this comprehensive blog post, I will delve into the historical context, current trends, and future projections of India’s coffee industry, supported by data, expert opinions, and real-world examples.
India’s Coffee Industry Historical Context
India’s tryst with coffee dates back to the 17th century when Baba Budan, a Sufi saint, smuggled seven coffee beans from Yemen and planted them in the hills of Chikmagalur, Karnataka. Since then, coffee cultivation has spread across the southern states of Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu, which account for nearly 98% of India’s coffee production.
The British played a pivotal role in commercializing coffee cultivation in India during the colonial era. However, it was only after independence that the Indian government took proactive measures to support the industry. The establishment of the Coffee Board of India in 1942 and the introduction of the Coffee Act in 1942 provided a regulatory framework for the industry’s growth.
“Coffee came to India well before the East India company, and until the middle of the 19th century, India was the only source of coffee for all of Europe,” explains Sunalini Menon, CEO of Coffee Lab Limited. youtube
Market Size, Growth & Trends
India is currently the sixth-largest producer and fifth-largest exporter of coffee globally. According to the Coffee Board of India, the country produced 320,000 metric tons of coffee in 2020-21, a 12% increase from the previous year. Exports also grew by 15% to 334,000 metric tons, valued at USD 846 million.
The domestic consumption of coffee in India has also been on the rise, driven by a growing middle class, urbanization, and changing lifestyle preferences. The per capita coffee consumption in India has increased from 78 grams in 2010 to 115 grams in 2020. As Nandan Nilekani, co-founder of Infosys, rightly pointed out, “The Indian coffee house culture is a reflection of the changing aspirations and lifestyles of young India”.
Major Regions & Geographic Breakdown
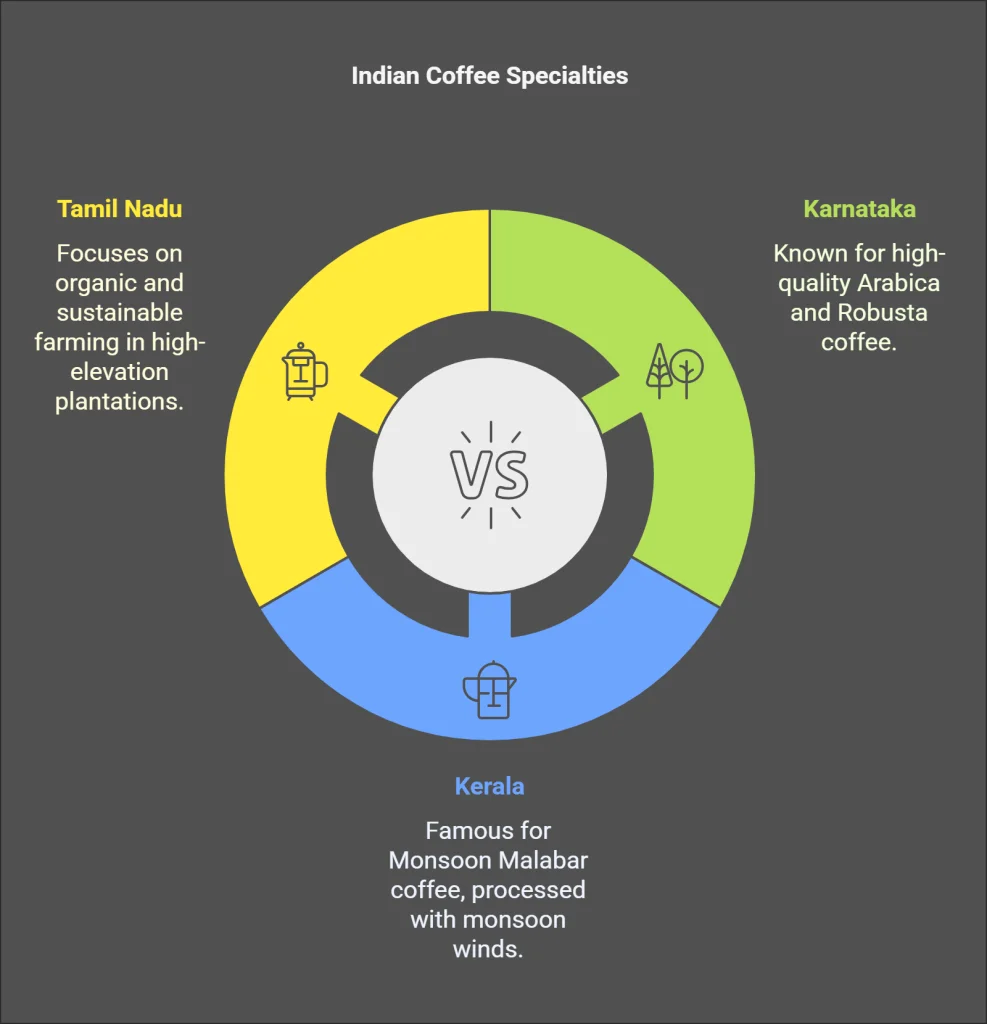
Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu are the primary coffee-growing states in India, with Karnataka alone accounting for 71% of the total production. The unique climatic conditions, characterized by high altitudes, ample rainfall, and well-drained soil, make these regions ideal for coffee cultivation.
- Karnataka: Known for its high-quality Arabica and Robusta beans, Karnataka’s coffee is grown primarily in the districts of Chikmagalur, Kodagu, and Hassan. The region is famous for its shade-grown coffee, which thrives under the canopy of rosewood, teak, and fig trees.
- Kerala: The state is renowned for its Monsoon Malabar coffee, a unique process where harvested beans are exposed to the monsoon winds, resulting in a distinct flavor profile. Wayanad, Travancore, and Nelliampathy are the primary coffee-growing regions in Kerala.
- Tamil Nadu: Coffee cultivation in Tamil Nadu is concentrated in the Nilgiris district, known for its high-elevation plantations and shade-grown coffee. The region produces both Arabica and Robusta varieties, with a focus on organic and sustainable farming practices.
Karnataka is the largest producer of coffee in India. The state is known for its high-quality Arabica and Robusta coffee beans and accounts for around 60% of India’s total coffee production. The coffee cultivation in Karnataka is mostly grown in the hilly regions of Chikmagalur, Coorg, and the Baba Budan hills.
Other major coffee-producing states in India include Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Andhra Pradesh. Indian coffee is known for its rich taste, aroma, and quality and is exported to various countries around the world.
The coffee industry in India plays an important role in the economy and provides employment opportunities to a large number of people, especially in rural areas. The government and various coffee organizations are working to promote and develop the coffee sector in India and improve the livelihoods of coffee farmers.
Supply Chain & Key Players in India’s Coffee Industry
India’s coffee supply chain involves a complex network of stakeholders, including small-scale farmers, cooperatives, private estates, Coffee wholesaler exporters, and domestic retailers. The Coffee Board of India plays a crucial role in regulating the industry, providing support to farmers, and promoting Indian coffee globally.
Some of the key players in India’s coffee industry include:
- Tata Coffee Limited: India’s largest integrated coffee company, with a presence across the value chain from plantations to retail.
- CCL Products (India) Limited: A leading exporter of instant coffee, supplying to global brands like Starbucks and Nestle.
- Nescafé: Nestle’s popular instant coffee brand, which has a strong presence in the Indian market and sources a significant portion of its coffee from the country.
Export & Trade Dynamics
India exports coffee to over 70 countries, with the European Union, Russia, and the United States being the primary markets. In recent years, there has been a growing demand for Indian coffee in emerging markets like Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
The Indian government has been proactive in supporting coffee exports through various initiatives, such as the “Brand India” campaign and the establishment of the Coffee Export Promotion Council. Free trade agreements with countries like South Korea and the ASEAN region have also helped boost coffee exports.
India Regulatory & Government Policies of the coffee industry
The Coffee Board of India, under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, is responsible for the regulation, development, and promotion of the coffee industry. The board sets quality standards, provides subsidies and incentives to farmers, and facilitates research and development activities.
The Indian government has also implemented various schemes to support coffee growers, such as the “Coffee Debt Relief Package” and the “Coffee Development Programme”. These initiatives aim to improve productivity, enhance quality, and promote sustainable farming practices.
Sustainability & Social Responsibility
Sustainability and social responsibility have become increasingly important aspects of India’s coffee industry. Many coffee growers and companies have adopted eco-friendly practices, such as shade-grown cultivation, rainwater harvesting, and the use of organic fertilizers.
Fair trade and ethical sourcing have also gained traction, with organizations like the Fair Trade Alliance Kerala (FTAK) working towards ensuring better prices and working conditions for small-scale farmers. As consumer awareness grows, sustainability has become a key differentiator for Indian coffee brands in both domestic and international markets.
I’m super bullish on coffee in India. Speciality coffee is a recently discovered (<10 years) trend in India. For years we were drinking those instant stuff.
Even if you check the engagement on this sub, the activity has picked up, and more and more ppl are consuming specialty coffee. If my forecast goes right, coffee industry in India will pick up pace in the next few years and in the next five years will be able to cross a billion mark 🤞
Innovation & Technology
The Indian coffee industry has been embracing innovation and technology to improve productivity, quality, and sustainability. Some notable developments include:
- Precision agriculture: The use of satellite imagery, drones, and sensor-based systems to optimize crop management and resource utilization.
- Blockchain technology: The implementation of blockchain-based traceability systems to ensure transparency and authenticity in the coffee supply chain.
- Value-added products: The development of innovative coffee-based products, such as coffee-infused beverages, snacks, and personal care items, to cater to evolving consumer preferences.
Competitive Landscape
India faces competition from other major coffee-producing countries, such as Brazil, Vietnam, and Colombia. However, Indian coffee has carved a niche for itself in the global market, thanks to its unique flavor profiles, shade-grown cultivation, and sustainable practices.
Within the domestic market, there is a growing competition among coffee brands and retail chains to capture the expanding consumer base. Homegrown brands like Café Coffee Day and Indian Coffee House compete with international players like Starbucks and Costa Coffee.
Challenges & Risks
Despite its growth and potential, the Indian coffee industry faces several challenges and risks:
- Climate change: Erratic weather patterns, rising temperatures, and changing rainfall patterns pose significant threats to coffee cultivation.
- Price volatility: Fluctuations in global coffee prices can impact the profitability and sustainability of coffee growers and exporters .
- Infrastructure and logistics: Inadequate infrastructure and inefficient supply chain management can lead to quality deterioration and increased costs .
- Labor issues: The coffee industry is labor-intensive, and ensuring fair wages and working conditions for farmworkers remains a challenge .
India Coffee Industry Future Outlook
India’s coffee industry is poised for significant growth in the coming years, driven by increasing domestic consumption, rising exports, and a focus on value-added products. As per industry projections, India’s coffee production is expected to reach 400,000 metric tons by 2025, with exports surpassing USD 1 billion.

To capitalize on this growth potential, the Indian coffee industry should focus on the following strategic recommendations:
- Invest in research and development to improve productivity, quality, and resilience to climate change.
- Strengthen the domestic market by promoting coffee culture, expanding retail presence, and developing innovative products.
- Enhance the brand image of Indian coffee in international markets through targeted marketing campaigns and participation in global trade events.
- Promote sustainable and ethical practices to meet the growing consumer demand for responsibly sourced coffee.
- Leverage technology and digital platforms to improve supply chain efficiency, traceability, and customer engagement.
FAQ
1- What are the main types of coffee grown in India?
India primarily grows Arabica and Robusta coffee. Arabica constitutes 70% of production and Robusta 30%.
2- How does Indian coffee differ in taste from other origins?
Indian coffee is known for its full-bodied, low-acidity profile with notes of spice, nuts and chocolate. Monsooned Malabar is a specialty coffee with a distinctive earthy flavor.
3- What is the harvesting season for coffee in India?
In India, coffee is harvested between November and February. Arabica is harvested in December to January, while Robusta is picked between January to February.
4- How can I best experience India’s coffee culture?
Visit the coffee-growing regions of Coorg and Chikmagalur in Karnataka, tour coffee plantations, and experience coffee tasting sessions. Explore artisanal cafes in metro cities for specialty coffee.
5- What sustainability certifications are common for Indian coffee?
Popular sustainability certifications for Indian coffee include Fairtrade, UTZ, Organic, and Rainforest Alliance. These indicate environmentally-friendly and ethical cultivation practices.
6- Where can I buy specialty Indian coffee beans?
Specialty Indian coffee is available on e-commerce websites like Something’s Brewing, The Coffee Barn, and Blue Tokai Coffee Roasters. Cafe Coffee Day and Tata Coffee also sell their premium coffees online.
7- What makes Indian coffee unique?
Indian coffee is known for its distinct flavor profiles, which can be attributed to the country’s unique growing conditions. The shade-grown cultivation method, where coffee plants are grown under a canopy of trees, imparts a mild and less acidic taste to the beans. Additionally, the monsoon processing technique, where harvested beans are exposed to monsoon winds, results in a unique flavor and aroma.
8- How does the Coffee Board of India support coffee growers?
The Coffee Board of India provides a wide range of support services to coffee growers, including:
Subsidies for the establishment of new plantations and the replanting of old ones
Financial assistance for the adoption of sustainable farming practices and quality improvement measures
Research and development activities to improve crop productivity and resilience
Training and extension services to promote best practices in coffee cultivation and processing
Marketing and promotional activities to enhance the visibility and demand for Indian coffee
9- What are the major challenges faced by small-scale coffee farmers in India?
Small-scale coffee farmers in India face several challenges, such as:
- Low productivity due to limited access to modern farming techniques and inputs
- Price volatility and lack of bargaining power in the market
- Climate change and weather-related risks
- Limited access to credit and financial services
- Inadequate infrastructure and transportation facilities
10- How is the Indian government promoting sustainable coffee cultivation?
The Indian government, through the Coffee Board of India, has been implementing various initiatives to promote sustainable coffee cultivation, such as:
- The “Sustainable Coffee Program” which provides financial incentives for the adoption of eco-friendly practices like shade-grown cultivation and rainwater harvesting
- The “Organic Coffee Production” scheme which supports farmers in transitioning to organic farming methods
- The “Coffee Quality Upgradation” program which focuses on enhancing the quality of coffee through improved harvesting and processing techniques
11- What role do cooperatives play in the Indian coffee industry?
Cooperatives play a crucial role in the Indian coffee industry by:
- Providing small-scale farmers with collective bargaining power and better access to markets
- Facilitating the sharing of knowledge, resources, and best practices among members
- Enabling farmers to achieve economies of scale in procurement, processing, and marketing
- Promoting sustainable and ethical practices through certifications like Fair Trade and Rainforest Alliance
12- How has the COVID-19 pandemic affected the Indian coffee industry?
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the Indian coffee industry, leading to:
- Disruptions in the supply chain and logistics, affecting the movement of coffee from farms to markets
- Reduced demand from the hospitality sector due to lockdowns and travel restrictions
- Labor shortages and increased costs due to safety measures and migration of workers
- Delayed payments and cash flow issues for farmers and exporters
However, the industry has shown resilience by adapting to the changing circumstances, focusing on direct-to-consumer sales, and leveraging e-commerce platforms.
13- What are some of the innovative coffee-based products emerging in India?
Some of the innovative coffee-based products gaining popularity in India include:
- Ready-to-drink coffee beverages in various flavors and formats
- Coffee-infused snacks like cookies, cakes, and energy bars
- Coffee-based personal care products like soaps, scrubs, and face masks
- Coffee-flavored beer and cocktails
- Coffee-based health supplements and nutraceuticals
These products cater to the evolving tastes and preferences of Indian consumers, particularly the younger generation.
14- How is technology transforming the Indian coffee industry?
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in the Indian coffee industry, with applications like:
- Precision agriculture using satellite imagery, drones, and sensor-based systems to optimize crop management
- Blockchain-based traceability systems to ensure transparency and authenticity in the supply chain
- E-commerce platforms and mobile apps for direct-to-consumer sales and customer engagement
- Data analytics and artificial intelligence for demand forecasting, quality control, and risk management
The adoption of these technologies is helping the industry to become more efficient, transparent, and responsive to market demands.
15- What are the major export destinations for Indian coffee?
The major export destinations for Indian coffee include:
- European Union countries like Italy, Germany, and Belgium
- Russia and other CIS countries
- United States and Canada
- Middle Eastern countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE
- Southeast Asian countries like Indonesia and Malaysia
India’s coffee exports have been growing steadily in recent years, thanks to the increasing recognition of the quality and unique characteristics of Indian coffee in the global market.
16- What are the key factors driving the growth of coffee consumption in India?
The key factors driving the growth of coffee consumption in India include:
- Rising disposable incomes and changing lifestyles of the middle class
- Growing urban café culture and the popularization of specialty coffee
- Increasing health consciousness and the perception of coffee as a healthier alternative to tea
- Influenced by Western trends and the global popularity of coffee chains like Starbucks and Costa Coffee
- Expansion of the organized retail sector and the availability of a wide range of coffee products
The Indian coffee market is expected to continue its growth trajectory in the coming years, driven by these factors and the increasing preference for premium and value-added coffee products.




